
5 Ways Digital Finance in the Philippines is Flourishing Despite Hurdles
by Johanan Devanesan January 17, 2024The digital finance landscape in the Philippines is undergoing a significant transformation, offering a plethora of opportunities for growth and innovation. The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) is at the forefront of this change, embracing global central banking standards and transitioning towards a digital financial ecosystem. This shift is not only about enhancing the efficiency of transactions but also about ensuring financial inclusivity across the nation, especially in remote areas.
In addition to these governmental efforts, a study by Google, Kantar, and Sixth Factor sheds light on the changing financial consumer behavior in the Philippines. This study underscores a growing inclination towards saving and investing, concerns about the safety of digital finance, and the reliance on online searches for financial information and services.
Despite the eagerness to engage with digital financial services, there remains a portion of the population that is cautious, mainly due to safety concerns. However, these concerns are gradually being addressed through user-friendly platform designs and educational initiatives in the Philippines, enhancing the overall confidence in digital finance.
Furthermore, the digital finance shift in the Philippines manifests differently among various banking segments. The unbanked, which constitute a significant portion of the adult population, are increasingly accessing digital finance services for the first time, primarily through mobile devices.
The underbanked segment, typically less affluent and digitally savvy, seeks reassurance and education to adopt new financial products confidently. Furthermore, the fully banked segment is actively seeking ways to grow wealth through more complex, riskier investments, showing a high level of digital finance engagement.
Here are five ways digital finance is growing in Philippines in spite of challenging macroeconomic factors.
High adoption of digital banking and fintech apps
A recent survey conducted by Capstone-Intel has revealed that a significant majority of Filipinos are increasingly opting for digital finance, finding it to be a convenient choice within the financial landscape of the Philippines.
The survey showed that 90% of participants have noticed a shift towards the use of digital banking and fintech apps. GCash, with 94%, was identified as the most popular choice among a substantial number of users. This was followed by PayMaya (39%), ShopeePay (26%), various bank applications (18%), GrabPay (8%), and other fintech apps (5%), in that order.
Conversely, 2% of the respondents stated they do not use any banking or fintech apps whatsoever.

Ella Kristina Domingo-Coronel
Ella Kristina Domingo-Coronel, Research and Publications Director at Capstone-Intel, commented on the survey’s implications:
“As we can see, even ’sari-sari’ stores now have a digital financing option for their customers. This means that accessibility and availability are there. That’s why, even though these fintech applications are owned by the private sector, the national government has to enhance the country’s finance technology infrastructure, including the measures that safeguard consumers in order to ensure the safety of Filipinos.”
Analysing the importance of these findings, the results highlight the need to develop even stronger financial technology infrastructure. With the prevailing increase in digital finance options across the Philippines, it becomes crucial for the government to step up and ensure regulated safety. Ella added,
“I would say that we still have to promote the utilisation of digital financing in the Philippines in order to weaken the negative outlook of the public about this option and normalise the usage of these fintech applications for us to amplify public confidence in digital financing.”
Startups fueling long-term remittances growth
With nearly 2 million Filipinos living abroad in 2021, per the Philippine Statistics Authority, the Philippines is a major player in the global remittance arena, ranking among the top countries in terms of inbound remittances. New market entrants are raising capital to meet this demand, despite a much more repressed funding climate globally.
A recent report from ResearchAndMarkets.com has shown that the international inbound remittance market in the Philippines grew by 2% in 2022, reaching US$ 38.04 billion in 2023. Similarly, the international outbound remittance market in the Philippines saw a 14.8% increase in 2022, amounting to US$188.5 million in 2023.
However, a slowdown in the growth of remittance inflows is anticipated in 2023 due to the economic deceleration in several key source countries. The World Bank attributes this decline to reduced migration and a global economic slowdown, estimating that total remittances will grow by about 2.5% to reach US$39 billion in 2023.
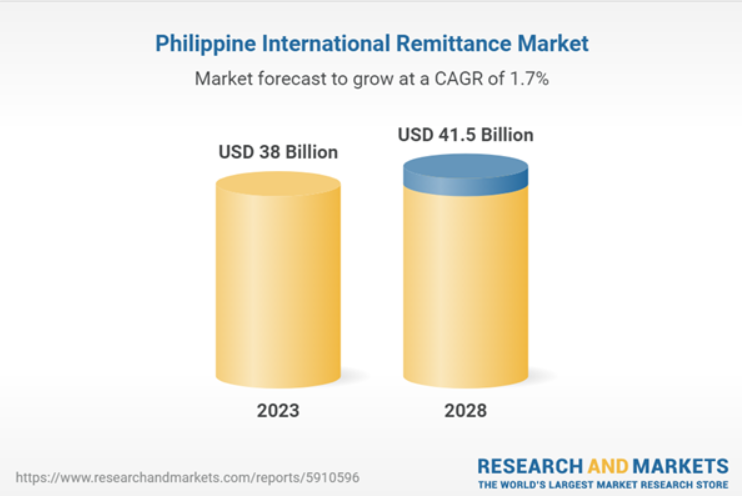
Despite this short-term outlook, the long-term prospects remain positive with emerging collaborations in the Philippine market, where strategic partnerships are becoming increasingly common. In October 2023, US-based fintech firm Circle announced a collaboration with Philippine company Coins.ph to facilitate remittances using USDC, offering low transaction costs and simplified processes.
Netbank, a banking-as-a-service platform, has also formed strategic alliances with international remittance companies to introduce a new service for remittances into the Philippines. This includes a partnership with UK-based TransferGo.
TANGGapp, short for Tap and Go Global App, has recently raised US$2.5 million in seed funding from various investors. The app facilitates low-amount money transfers from the US to the Philippines and allows users to link local bank accounts and digital wallets. Over the past two years, TANGGapp has experienced a 25-fold growth, with a repeat usage rate of 48%.
As the global remittance market is set to grow substantially in the next few years, Philippine-based startups are looking to expand internationally. BayaniPay, a fintech and remittance startup, is planning to establish a presence in Canada following a successful seed funding round of US$2.1 million, bringing its total funding to US$6.6 million. The company, which currently serves areas in the USA, has seen significant growth in its transaction values and user base in 2023.
With over a million Filipinos residing in Canada, BayaniPay’s expansion is expected to further increase its transaction volumes, contributing to the overall growth of the remittance market in the Philippines.
Transactions going cross-border, in real-time
The shift to real-time cross-border payments represents a significant necessary leap forward for banks in the Philippines, with the central bank BSP mandating under its Digital Payments Transformation Roadmap, that 50% of total retail payments in the country will be converted to electronic channels by last year.
The forward-looking BSP has also established cross-border payment agreements with other countries to facilitate cross-border trade, investment, tourism for Philippines businesses as well as to power remittance flows for the millions of Filipinos working abroad.

Cross-border payments market share, where fintechs and disruptors are displacing traditional financial institutions
The central bank signed two agreements with the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) to integrate the Philippines’ InstaPay and Singapore’s PayNow real-time payment networks in 2021, leveraging both countries’ QR standards to fast-track payments connectivity between the two nations.
This was followed shortly by the central banks of Philippines, Malaysia, and Thailand examining cross-border payment agreements to link their QR and real-time payment systems, before inking a pact with its neighbors Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand to boost connectivity and ease payment flows between the five ASEAN countries.
BSP governor Felipe M. Medalla believes payment connectivity between the five largest economies of ASEAN could be implemented within the next two to three years. The initiative will seek to deepen financial integration and facilitate inter-regional trade by enabling faster, cheaper and more transparent cross-border transactions.
‘Cashless’ payments maturing
A key indicator of the digital finance pivot in the Philippines is the rise in digital payment usage, which has seen a substantial increase in recent years. The 2022 Status of Digital Payments BSP Report highlighted that 42.1% of total retail payments by volume were digital, marking a significant uptick from the previous year.
The BSP is championing several initiatives to further this digitalisation, such as the polymerisation of Banknotes and the Paleng-QR Ph Plus Programme, aimed at encouraging digital payments in various sectors including local markets and public transportation. Most public services in the Philippines have been mandated to accept digital payments, with some like the Philippines Securities and Exchange Commission accepting only digital transactions since 2023.
Moreover, the Philippine government’s initiatives to promote a ‘cashless society’ have played a crucial role in this shift. By encouraging digital transactions, the government aims to enhance financial inclusivity and streamline economic processes.
The launch of the PESONet and InstaPay automated clearing houses has facilitated real-time, affordable, and efficient fund transfers between financial institutions. These platforms have seen exponential growth in usage, with transactions reaching millions daily. Over PHP5 trillion of transactions were recorded through PESONet and InstaPay last year.
Fastest-growing ASEAN economy prioritises financial inclusion
The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report, released in January 2024, forecasts that the Philippines’ gross domestic product (GDP) will grow by 5.8% this year, slightly up from an estimated 5.6% in 2023.
Should the World Bank’s forecast for the Philippines materialise, the country would be the fastest-growing economy in Southeast Asia this year, tied with Cambodia, which is also expected to see a 5.8% growth.
The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) recognises that digital finance initiatives are contributing to the Philippines exceeding expectations, despite challenges, in achieving its financial inclusion goals and development plans.
BSP Governor Eli M. Remolona, Jr stated in 2023,

Eli M. Remolona, Jr
“We have seen depositors improve their lives from gaining access to other financial services, such as loans, insurance, and investments. For instance, insurance helps farmers recover faster from losses inflicted by natural calamities, while small business loans help microentrepreneurs expand or pivot their businesses.
“Indeed, while we have a long way to go in our financial inclusion journey, millions of Filipinos are already benefitting from our multi-pronged financial inclusion initiatives.”
Financial inclusion in the Philippines has markedly improved in recent years alongside its economic growth. Between 2019 and 2021, the number of Filipino adults with a financial account more than doubled from 20.9 million to 42.9 million, as per BSP data. Consequently, more than half (around 56%) of all adults in the country were banked by 2021, a substantial increase from just 29% in 2019. Despite this progress, 34.3 million adults remained without bank accounts.
As part of the BSP’s Digital Payment Transformation Roadmap 2020-2023, the central bank aimed to include 70% of adult Filipinos in the financial system and digitise 50% of all retail payments by the end of 2023.
The country was reportedly on track to achieve these objectives earlier in 2023, according to former BSP Governor Felipe Medalla. He highlighted that e-wallets and recent initiatives have been instrumental in integrating many Filipinos into the formal banking system, encouraging the adoption of digital financial services, and transitioning towards digital payments.
This ongoing digital financial revolution across the country signifies a new era of financial opportunity and inclusion, marking a notable shift from traditional banking methods to a more accessible, efficient, and inclusive digital finance system in the Philippines.
Featured image credit: Edited from freepik








